Detailed Introduction
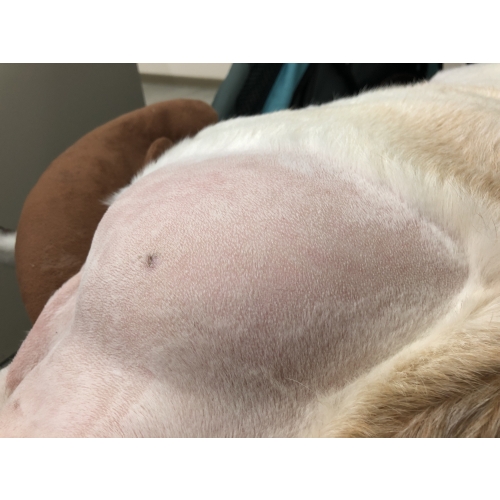
Lipoma is one of the common benign tumors. It often grows between subcutaneous and muscles. It is detected when the owners observe or touch their pets. Except for the issue of appearance, it generally has little effects on pets’ life. Like human lipomas, there is no clear cause, but it is speculated to be related to pet's age, family genes, food type, and obesity. It occurs more often in middle-aged and elderly pets, less related to breed, gender, and body type. The majority of lipomas are benign tumors, and usually grow on body surface areas, such as limbs and trunk; however, some minority may also grow between muscles and blood vessels.
There are three types of lipomas:
- Benign lipoma, with tumor capsules, tumor surface is light yellow color, can slide if pressure is applied on body surface, soft texture, low local invasiveness, low metastasis rate, can be singular tumor (the appearance of one tumor) or multiple tumors (the appearance of several tumors).
- Infiltrative lipoma is a benign lipoma with low metastasis rate but high local invasiveness. This type of lipoma has no tumor capsules and can be very large in volume, can invade surrounding muscles, blood vessels, and bones and other tissues, and often cause local dysfunction in pets. If it affects pets’ lives, owners are usually advised to consider resection. However, as there is no tumor capsule, the boundary of the tumor is unclear, it often recurs because it cannot be completely removed.
- Liposarcoma is a malignant lipoma that is locally invasive and may metastasize to the organs.
Lipoma removal is recommended for following situations:
Lipoma is malignant, lipoma is infiltrative or benign but compresses nerves or blood vessels, affecting pets’ life, and grows faster. Lipomas are usually removed by surgery. For the treatment of infiltrative lipomas with inconspicuous borders or malignant lipomas, complementary therapy may be added to inhibit the recurrence of residual tumor cells.
Lipoma is malignant, lipoma is infiltrative or benign but compresses nerves or blood vessels, affecting pets’ life, and grows faster. Lipomas are usually removed by surgery. For the treatment of infiltrative lipomas with inconspicuous borders or malignant lipomas, complementary therapy may be added to inhibit the recurrence of residual tumor cells.